In these captivating winter settings of the United States, where the flora and fauna transform into a glistening wonderland, a silent and often undervalued threat waits beneath the beauty of the winter season – hypothermia. As we celebrate in the allure of snow-covered landscapes and cozy winter evenings, understanding the chilling dashes of realism of hypothermia becomes paramount especially for the elderly, children and homeless. This article takes a comprehensive journey through the statistics, data, and nuances of hypothermia, shedding light on its silent danger and offering insights to navigate the cold with caution and awareness.
Hypothermia: A Stealthy Menace
Hypothermia is a condition characterized by a dangerous drop in body temperature. It occurs when the body loses heat faster than it can produce it, leading to a state of decreased core temperature. Often, this silent adversary interrupts quietly, challenging the body’s natural mechanisms for maintaining a healthy and normal temperature.
Hypothermia can affect anyone, but certain populations, such as the elderly, toddlers and those experiencing homelessness, are particularly more vulnerable. Understanding the signs, symptoms, and risk factors is crucial to recognizing and addressing this potentially life-threatening condition.
The Stark Reality: Statistics and Data
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provide a detailed perspective on the prevalence of hypothermia-related deaths in the United States. With over 1,300 fatalities reported annually due to exposure to extreme cold, the statistics underscore the severity of this condition.
It’s essential to acknowledge that these numbers represent not just data points but lives impacted by a condition that often goes unnoticed amidst the winter’s charm. The gravity of hypothermia demands our attention and prompts us to delve deeper into its intricacies.
Signs, Symptoms, and the Subtle Onset
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of hypothermia is crucial for early intervention. The condition doesn’t always announce itself with dramatic shivering; it can start subtly, making vigilance paramount.
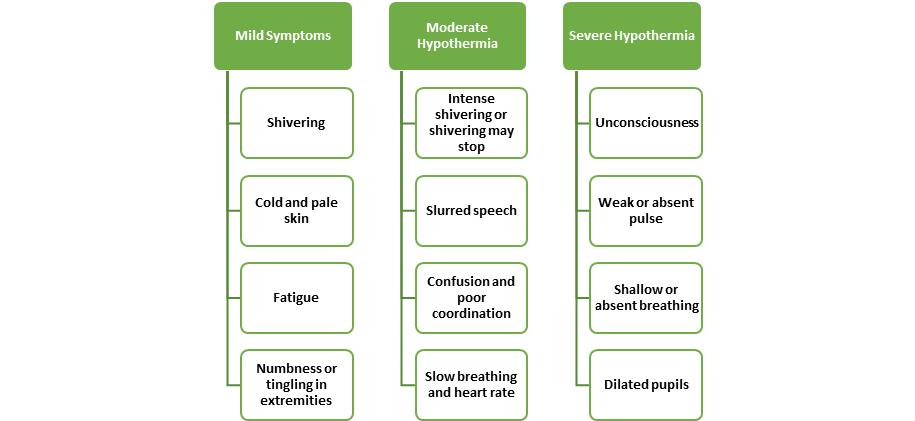
Early symptoms may include shivering, fatigue, and confusion. As hypothermia progresses, more severe symptoms manifest, such as slurred speech, shallow breathing, and a weak pulse. Being aware of these indicators empowers individuals to take proactive measures to address the condition promptly.
As hypothermia progresses, so does its severity. Moderate hypothermia presents a more critical situation, with increased risk to the individual’s well-being. Recognizing the signs and taking appropriate action becomes crucial at this stage.
Severe hypothermia is a life-threatening condition that demands immediate intervention. Understanding the signs and acting promptly can be the difference between life and death in this critical stage. The Symptoms of various stages are following:
Winter’s Cold Embrace: A Co-Conspirator in Hypothermia
While hypothermia can occur in various environments, winter’s icy breath and biting winds significantly contribute to its prevalence during the colder months. The National Weather Service (NWS) emphasizes the impact of cold weather on the body’s ability to maintain a healthy temperature.
Factors such as wind chill exacerbate the rate at which the body loses heat, making it crucial to consider the “feels-like” temperature rather than just the ambient temperature. Additionally, wet conditions, whether from rain, snow, or wet clothing, increase the risk of hypothermia. Understanding these environmental factors is vital for gauging the potential danger and taking appropriate precautions.
Preventing Hypothermia: A Winter Survival Guide
Preventing hypothermia involves a combination of awareness, preparedness, and proactive measures. The American Red Cross provides valuable tips to stay warm and safe during cold weather, serving as a guide for winter survival:
- Dress in Layers: Wearing layers helps trap heat close to the body. This includes a moisture-wicking base layer, an insulating layer, and a waterproof outer layer to protect against wind and moisture.
- Stay Dry: Wet clothing or exposure to rain and snow significantly increase the risk of hypothermia. Wearing waterproof clothing and avoiding prolonged exposure to wet conditions is essential.
- Stay Informed: Monitoring weather forecasts, including wind chill factors, allows individuals to plan accordingly and avoid unnecessary exposure to extreme cold.
- Recognize Vulnerable Populations: Certain groups, such as the elderly and those experiencing homelessness, are more susceptible to hypothermia. Community outreach and support can play a crucial role in protecting these vulnerable populations.
Navigating Winter’s Embrace with Caution
As winter wraps its icy cloak around the nation, this article serves as a call to awareness and preparedness. Hypothermia is not just a term; it’s a reminder to respect the cold, understand its potential risks, and take proactive steps to safeguard ourselves and those around us.
In the symphony of winter, let knowledge be our guide. May our journey through the season be marked by warmth, safety, and an appreciation for the subtle dangers that accompany the beauty of the cold. By understanding hypothermia’s silent threat and taking preventive measures, we can navigate winter’s embrace with resilience and awareness, ensuring that the season remains a time of enchantment rather than a source of danger.

